Building a gRPC Web service
This document will show you how to build a browser/server application with Vert.x and gRPC Web.
What you will build
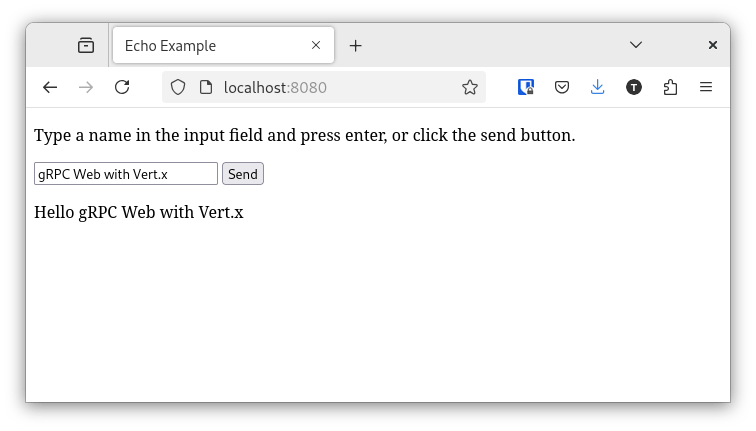
The application involves a client, the browser, and a Vert.x server:
-
the user types a name in a text field and clicks the send button
-
the browser sends the name to the server using the gRPC Web protocol
-
the server replies with a greeting
-
the browser displays the greeting
On the server side, you will create a Vert.x gRPC server service that:
-
implements a gRPC server stub
-
configures an HTTP server replying to both gRPC Web and static file requests
On the client side, you will create a web page that uses the gRPC Web Javascript client.

What you need
-
A text editor or an IDE
-
Java 17 or higher
You don’t have to install protoc or the protoc plugins like vertx-grpc-protoc-plugin2, protobuf-javascript and protoc-gen-grpc-web as they will be managed by a Maven plugin.
Create the project
gRPC service definition
The gRPC Greeter service consists in a single SayHello rpc method. The HelloRequest message contains the name sent by the client. The HelloReply message contains the greeting generated by the server.
service.proto filesyntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_package = "io.vertx.howtos.grpcweb";
option java_outer_classname = "HelloWorldProto";
package helloworld;
// The greeting service definition.
service Greeter {
// Ask for a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
// The request message containing the user's name.
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greeting
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}Code generation
From the service definition, several files must be generated:
-
Java message and server classes
-
Javascript files
-
gRPC Web specific (Javascript) files.
The protoc invocation is managed with the protobuf-maven-plugin.
protobuf-maven-plugin<plugin>
<groupId>io.github.ascopes</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<configuration>
<protocVersion>4.29.3</protocVersion>
<sourceDirectories>src/main/proto</sourceDirectories>
<javaEnabled>false</javaEnabled>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>compile-java</id>
<configuration>
<javaEnabled>true</javaEnabled>
<outputDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/java</outputDirectory>
<jvmMavenPlugins>
<jvmMavenPlugin>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-grpc-protoc-plugin2</artifactId>
<version>${vertx.version}</version>
<mainClass>io.vertx.grpc.plugin.VertxGrpcGenerator</mainClass>
<jvmArgs>
<jvmArg>--grpc-client=false</jvmArg>
<jvmArg>--grpc-service</jvmArg>
<jvmArg>--service-prefix=Vertx</jvmArg>
<jvmArg>--vertx-codegen=false</jvmArg>
</jvmArgs>
</jvmMavenPlugin>
</jvmMavenPlugins>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>generate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>compile-javascript</id>
<configuration>
<outputDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/web</outputDirectory>
<binaryUrlPlugins>
<binaryUrlPlugin>
<url>${protoc.gen.js.url}</url>
<options>import_style=commonjs</options>
</binaryUrlPlugin>
</binaryUrlPlugins>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>generate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>compile-javascript-web</id>
<configuration>
<outputDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/web</outputDirectory>
<binaryUrlPlugins>
<binaryUrlPlugin>
<url>${protoc.gen.grpc.web.url}</url>
<options>import_style=typescript,mode=grpcwebtext</options>
</binaryUrlPlugin>
</binaryUrlPlugins>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>generate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>| 1 | We choose to use the CommonJS modules generation style instead of closures. |
The server side
We need some dependencies for the project to compile:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-stack-depchain</artifactId>
<version>${vertx.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-grpc-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId>
<version>${protobuf.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-api</artifactId>
<version>${grpc.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-protobuf</artifactId>
<version>${grpc.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-stub</artifactId>
<version>${grpc.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>The server side code fits in a single ServerVerticle class.
First, the gRPC server stub implementation.
VertxGreeterGrpcService service = new VertxGreeterGrpcService() {
@Override
public Future<HelloReply> sayHello(HelloRequest request) {
return Future.succeededFuture(HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("Hello " + request.getName()).build());
}
};
GrpcServer grpcServer = GrpcServer.server(vertx);
grpcServer.addService(service);There is nothing specific to gRPC Web here.
GrpcServer enables the gRPC Web protocol support by default. |
Then we have to configure a Vert.x Web Router to accept both gRPC Web and static file requests.
Router router = Router.router(vertx);
router.route()
.consumes("application/grpc-web-text") (1)
.handler(rc -> grpcServer.handle(rc.request()));
router.get().handler(StaticHandler.create()); (2)
return vertx.createHttpServer()
.requestHandler(router)
.listen(8080);| 1 | All requests with application/grpc-web-text content type will be handed over to the grpcServer. |
| 2 | All other GET requests will be handled by a Vert.x Web StaticHandler. |
The client side
Before writing code, we must set up the project to build client side code. For simplicity, we choose to use the esbuild-maven-plugin. In a few words, it’s a Maven plugin that wraps esbuild, a fast bundler for the web.
A couple of dependencies are required, which we grab as Maven dependencies thanks to mvnpm:
esbuild-maven-plugin<plugin>
<groupId>io.mvnpm</groupId>
<artifactId>esbuild-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.0.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>esbuild</id>
<goals>
<goal>esbuild</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<entryPoint>index.js</entryPoint>
<outputDirectory>${project.build.outputDirectory}/webroot/js</outputDirectory> (1)
</configuration>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mvnpm</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-web</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mvnpm</groupId>
<artifactId>google-protobuf</artifactId>
<version>3.21.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>| 1 | webroot is the default base directory from where the Vert.x Web StaticHandler serves static files. |
The user interface code fits in a single index.html file.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Echo Example</title>
<script type="module">
import {sayHello} from "/js/index.js"; (1)
window.sayHello = sayHello; (2)
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>Type a name in the input field and press enter, or click the send button.</p>
<div class="input-group">
<!-- Invoke javascript function on submit -->
<form onsubmit="return sayHello();">
<input type="text" id="name">
<input type="submit" value="Send">
</form>
</div>
<p id="msg"></p>
</div>
</body>
</html>| 1 | Import the sayHello function from our Javascript module (see below). |
| 2 | Make the sayHello function global. |
Last but not least, let’s implement the sayHello function:
const {HelloRequest} = require("./service_pb"); (1)
const {GreeterClient} = require("./service_grpc_web_pb"); (2)
const greeterClient = new GreeterClient("http://" + window.location.hostname + ":8080", null, null); (3)
export function sayHello() {
const request = new HelloRequest();
request.setName(document.getElementById("name").value);
greeterClient.sayHello(request, {}, (err, response) => {
const msgElem = document.getElementById("msg");
if (err) {
msgElem.innerText = `Unexpected error for sayHello: code = ${err.code}` + `, message = "${err.message}"`;
} else {
msgElem.innerText = response.getMessage();
}
});
return false; // prevent form posting
}| 1 | Import the HelloRequest object from the Javascript generated file. |
| 2 | Import the GreeterClient object from gRPC Web (Javascript) generated file. |
| 3 | Configure the client to send requests to the web server. |
Running the application
You can run the application with Maven:
./mvnw compile exec:javaYou should see:
Server started, browse to http://localhost:8080
You can now browse to http://localhost:8080 and follow the instructions.
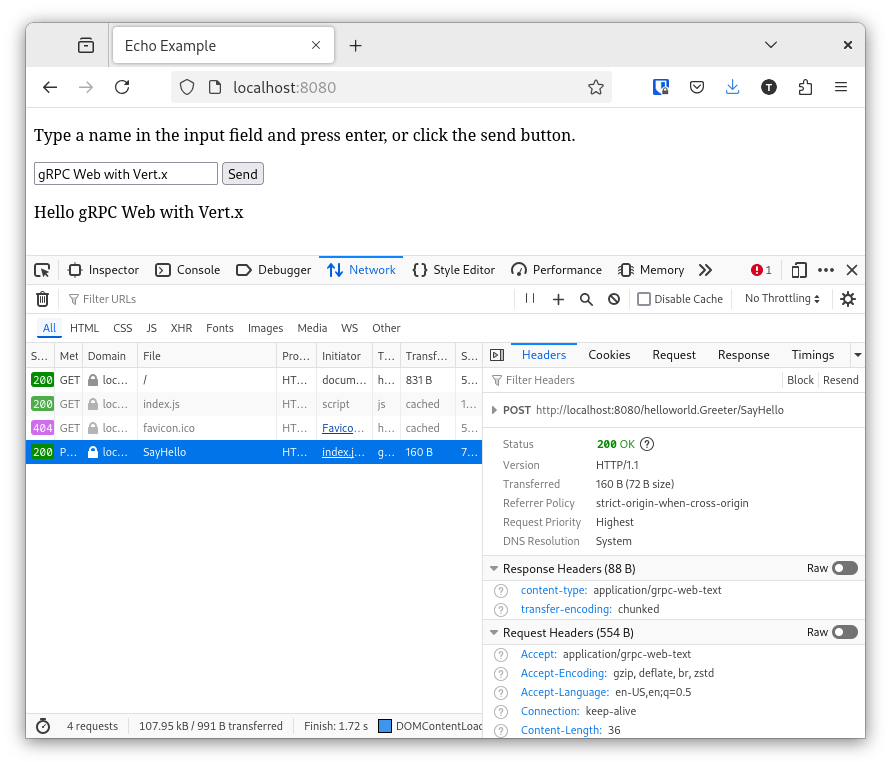
Use the dev tools of your browser to inspect the gRPC Web traffic.
Summary
This document covered:
-
implementing a Vert.x web server that replies to both static file and gRPC Web requests,
-
creating a web page that uses the gRPC Web client.