Eclipse Vert.x 4 milestone 3 released!
We are extremely pleased to announce the third 4.0 milestone release of Eclipse Vert.x .
Vert.x 4 is the evolution of the Vert.x 3.x series that will bring key features to Vert.x.
This release aims to provide a reliable distribution of the current development of Vert.x 4 for people who want to try it and provide feedback.
Futurisation
Vert.x 4 extends the 3.x callback asynchronous model to a future/callback hybrid model.
public interface NetClient {
// Since 3.0
void connect(int port, String host, Handler<AsyncResult<NetSocket>> handler);
// New in 4.0
Future<NetSocket> connect(int port, String host);
}This third milestone makes progress and coverts the following stack modules:
- vertx-service-discovery
- vertx-config
- vertx-circuit-breaker
Data object mapping for service proxies
Vert.x 3 service proxies is a lightweight layer on top of Vert.x Event-Bus providing typed contracts.
One can easily create a service on top of the Event-Bus.
@VertxGen
interface DateService {
// callback the handler with the current date
void date(Handler<AsyncResult<String>> handler)
}Service proxies request/response payload are of type JSON.
Of course service proxies allow to map beans to JSON using data objects but this comes with two caveats
- only JSON object can be mapped
- the data object must be a
@DataObjectannotated bean with atoJson()method and a JSON object constructor
In Vert.x 4 we extend the data object support to any Java class and any JSON type, e.g in this example
@VertxGen
interface DateService {
// encode the date with iso date format
@Mapper static String toJson(ZonedDateTime value) {
return ZonedDateTime.format(value);
}
// decode the date with iso date format
@Mapper static ZonedDateTime fromJson(String value) {
return ZonedDateTime.parse(value);
}
// callback the handler with the current date
void date(Handler<AsyncResult<ZonedDateTime>> handler)
}The generated code will then use these mappers to encode and decode JSON values.
For reusability mappers can also be java.util.function.Function instead, e.g
@Mapper Function<String, ZonedDateTime) fromJson = ZonedDateTime::parse;
@Mapper Function<ZonedDateTime, String> toJson = ZonedDateTime::toString;Mongo client GridFS
The client can store and retrieve files and binary data using MongoDB GridFS.
Future<String> fut = gridFsClient.uploadFile("file.name");
fut.setHandler(res -> {
if (res.succeeded()) {
String id = res.result();
//The ID of the stored object in Grid FS
} else {
res.cause().printStackTrace();
}
});The client can perform the usual CRUD operations on files and also provide bucket management.
Vert.x Web utilities
While the routing context will allow you to access the underlying request and response objects, sometimes it will be more productive if a few shortcuts would be present to help with common tasks. A few helpers are present in the context to facilitate with this task.
Serve an “attachment”, an attachment is a response that will trigger the browser to open the response on the OS application configured to handle a specific mime type. Imagine you’re generating a PDF:
routingContext
.attachment("weekly-report.pdf")
.end(pdfBuffer);Perform a redirect to a different page or host. One example is to redirect to an HTTPS variant of the application:
routingContext.redirect("https://securesite.com/");Send a JSON response to the client:
// no need to specify the content type headers
rc.json(new JsonObject().put("hello", "vert.x"));Simple content type check:
if (routingContext.is("application/json")) {
// ...
}Verify if a request is “fresh” with respect to the cache headers and the current values of last modified/ etag:
if (rc.isFresh()) {
// client cache value is fresh perhaps we
// can stop and return 304?
}Other changes
- Groovy has been simplified in Vert.x 4 to remove code generation that was not really needed in practice
- The original Redis client deprecated in 3.7 has been removed replaced by the new Redis client
- JSON changes
- Jackson databind is now an optional Maven dependency which means that applications need to explicitly add this dependency to the classpath
- Specific Jackson utility methods are moved to specific Jackson classes
- Vert.x can use an alternative implementation than Jackson for JSON encoding and JSON decoding
- The following components have reached their end of life and have been pruned
- MySQL / PostgreSQL async client replaced by the Vert.x SQL Client (since 3.8)
- AMQP bridge replaced by the Vert.x AMQP Client (since 3.7)
Ramping up to Vert.x 4
Instead of developing all new features exclusively in Vert.x 4, we introduce some of these features in the 3.x branch so the community can benefit from them. The Vert.x 4 development focus on more fundamental changes that cannot be done in the 3.x series.
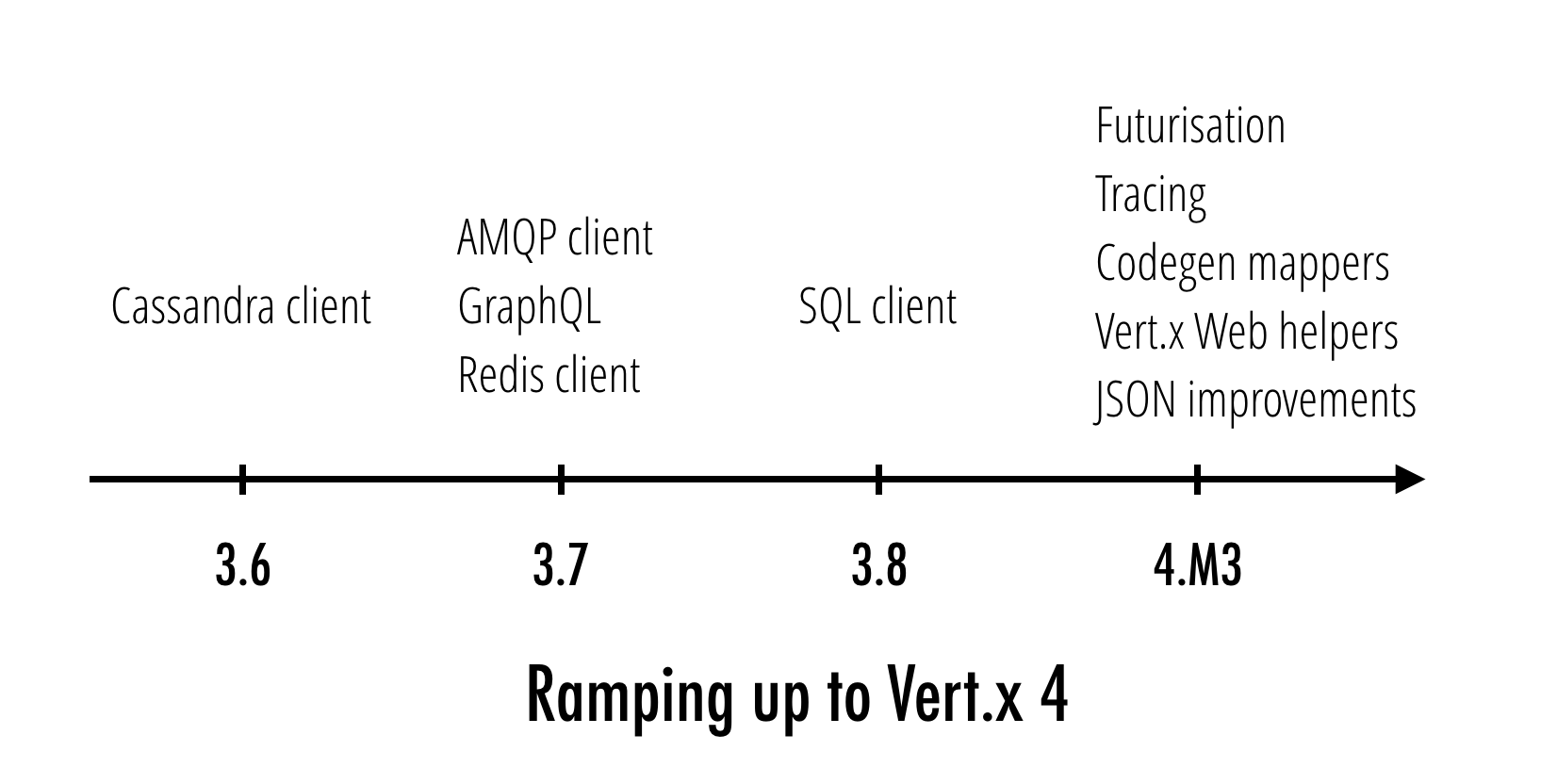
This is the third milestone of Vert.x 4, we aim to release Vert.x 4 by the end of this year and you can of course expect more milestones to outline the progress of the effort.
Finally
The deprecations and breaking changes can be found on the wiki.
For this release there are no Docker images.,
The release artifacts have been deployed to Maven Central and you can get the distribution on Maven Central.
You can bootstrap a Vert.x 4.0.0-milestone3 project using https://start.vertx.io.
The documentation has been deployed on this preview web-site https://vertx-ci.github.io/vertx-4-preview/docs/
That’s it! Happy coding and see you soon on our user or dev channels.




